Katowice will test several NBS that can be implemented at the micro-urban level
Katowice demo will implement a network of micro-location NBS, such as urban furniture (e.g. NBS-based benches and microalgae trees) and urban facility fixtures (green walls with pollutant-specific plants and vertical gardens) in public areas. The NBS will use native plant species (plants spontaneously growing on urban and industrial areas) and plants recommended for use in urban greenery.
Katowice is a Polish city in the Silesian Voivodeship, which is an important socio-economic point. Residents and visitors of Katowice study, work, relax and receive treatment in specialized hospitals. As a result, there is a high concentration of people in traffic and concrete surfaces that create an urban heat island that is extremely unfriendly to life, surrounded by busy streets where rainwater disappears into drains moments after rainfall.
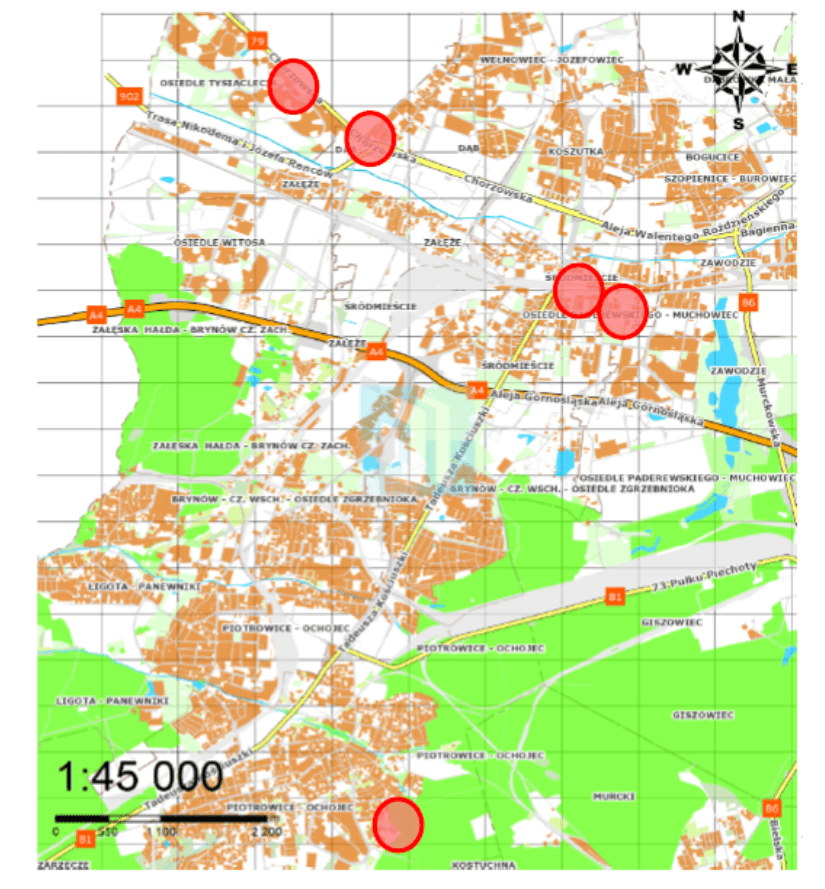
Katowice will create 5 pilot points – 4 green stops and an urban area in locations with high heat island indications for Katowice. The locations were chosen on city land. The green points will have diverse objectives:
- environmental (reducing heat island, increasing water retention, increasing biodiversity, providing other ecosystem services),
- social (positive impact on health and well-being),
- educational (test stations and information boards to educate the public about vegetation, retention, air pollution and causes of heat islands and mitigation measures).
Katowice has selected the following Nature Based Solution (NBS) points:
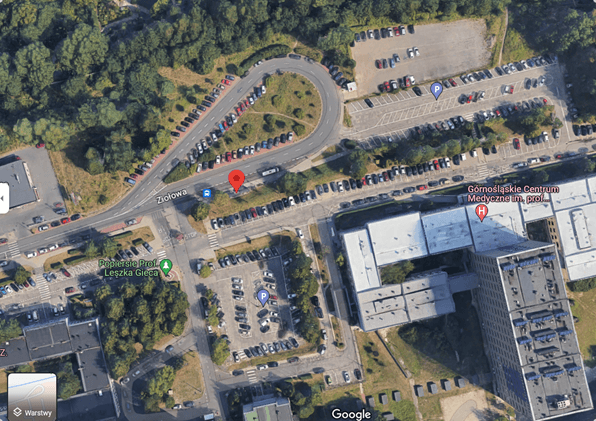
- Bus stop Ochojec – Hospital at Ziołowa Street in Katowice: the point is located next to a large parking lot, where the level of air pollution is high and the concrete surface promotes the formation of an urban heat island. Despite the high density of the site’s reinforcement, it will be possible to plant trees. The site will be landscaped with low green infrastructure in the form of shrubs, perennials and ornamental grasses. A sensory garden will also be created.
- Bus stop at Jagiellońska Street in Katowice: the spot is located among strictly built-up areas and the surface is made of pavement. The area will be unsealed and landscaped with greenery in the form of low shrubs, perennials, grasses and climbers, possible tree planting.
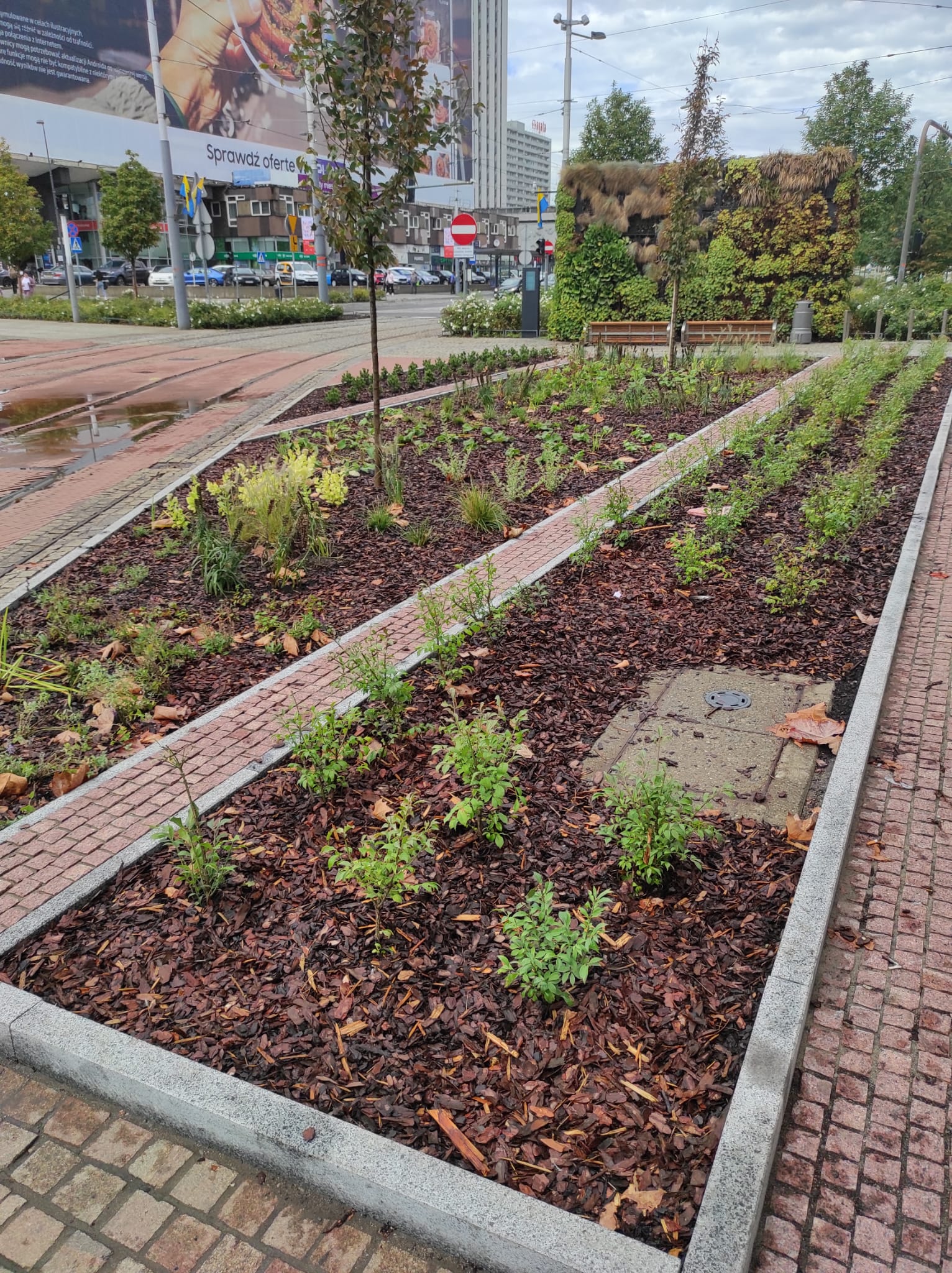
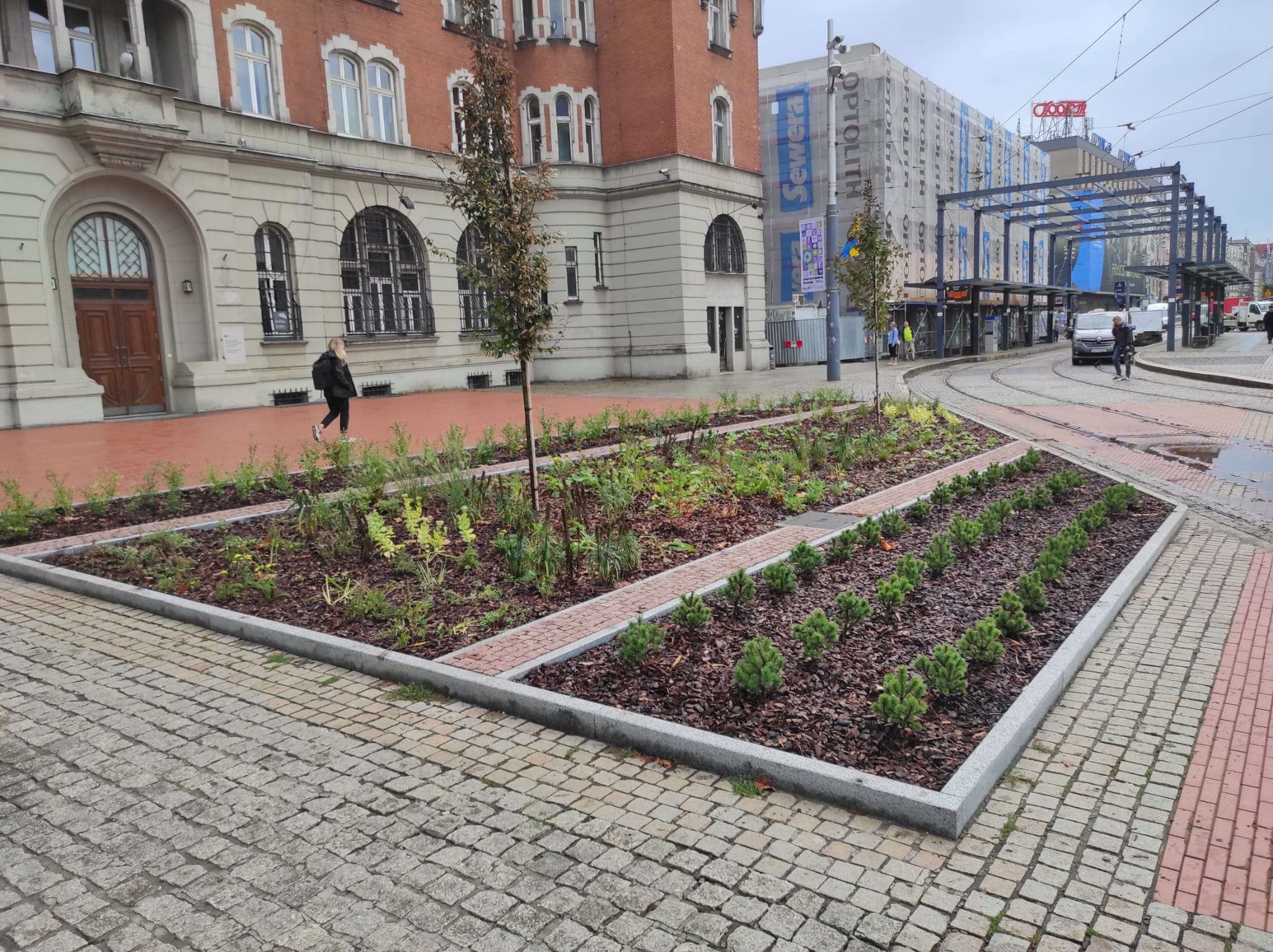
- Urban area between Korfantego Street and Market Square in Katowice: this area is located in the very center of the city, and is therefore surrounded by buildings and paved sidewalks. It is planned to unseal the pavement and introduce plantings compositionally related to the vegetation already developed in the area.
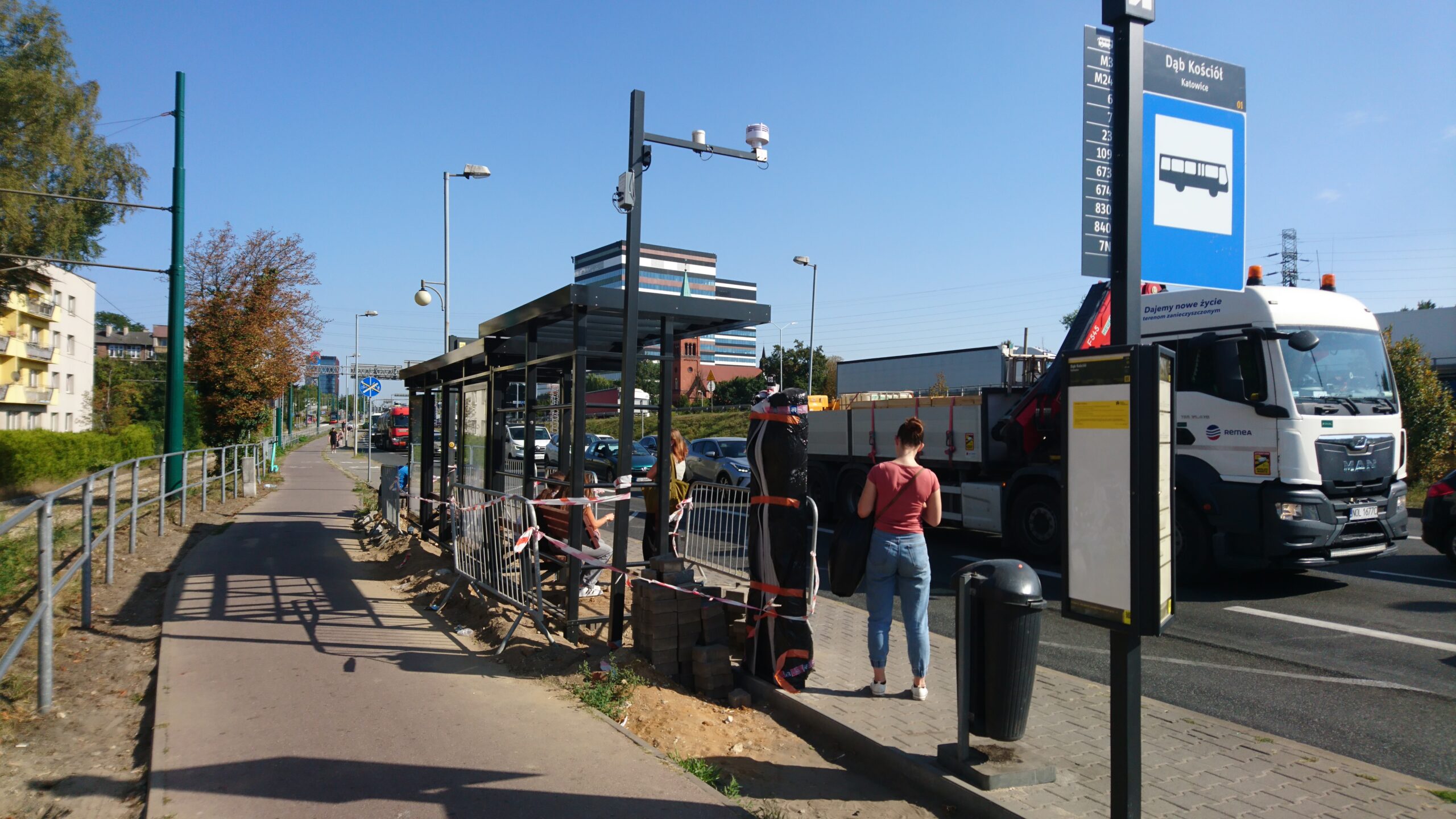
- Bus stop “Dąb Kościół” at Chorzowska Street in Katowice: the point is located on a very busy street and is therefore characterized by high noise, air pollution and urban heat island. Nature-based solutions (NBS) will be introduced, including ornamental shrubs, perennials, grass and climbers.
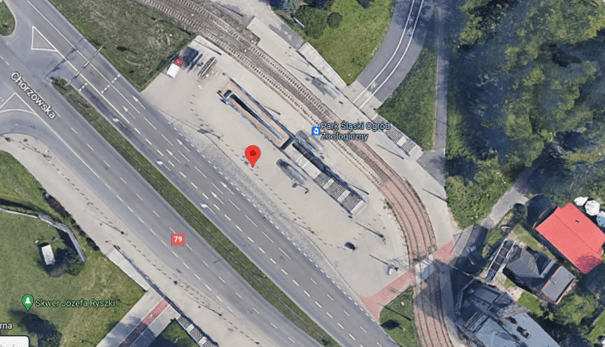
- Bus stop “Park Śląski Ogród Zoologiczny” at Chorzowska Street in Katowice: this site is very challenging due to the unfriendly terrain. A large number of green plants in the form of ornamental shrubs, perennials, grasses, climbers on supports will be introduced.
In addition, bus shelters at selected bus stops will be replaced with shelters with green roofs. The selected vegetation will be easy to maintain to minimize expenditures (including water, maintenance). The selected points, despite diverse challenges, including lack of shade, urban heat island phenomenon, high air pollution, lack of retention, high density of land reinforcement, noise, unfriendly landforms, will be model examples that can be implemented in other cities.
- Revitalization of areas – changing the character of urban areas to a greener one.
- Changing the microclimate and reducing extreme temperature.
- Increasing water retention by unsealing paved surfaces and providing greenery with positive effect on accumulation of water in the ground and in vegetation.
- Decreasing air pollution (including PM) and noise pollution through plant species acting as sound-absorbing barrier.
- Improving physical and mental health of inhabitants.
- Involving the public in the everyday ecological aspects of the city’s functioning.
NEW! Follow the Katowice demo storymap
Place Lab in Katowice
The local Competency Group in Katowice was formed in 2023 from the representatives of academia, civil society and economic sector who contribute to all five UPSURGE criteria. The kick-off meeting, when we presented the UPSURGE project, the role of Place Lab in Katowice and our ambitious plans, took place in October 2023. However, the first initial meeting for the people interested in joining the CG took place in July 2023.
During the second meeting in December 2023 we prepared the Operational Plan and we identified the following target groups: elderly people, local decision makers, district residents, children, journalists, who will be involved in our actions. We invited to join the meeting of Katowice Place Lab the representatives of some groups engaged in our UPSURGE actions: the Culture Centre in Dąb District, the hospital in Ochojec district, local authorities and other local activists. The Place Lab activities in Katowice started, with a huge engagement of the CG experts, in the beginning of 2024 and, in its first phase, focused on eco-sensitisation. After an open lecture on biophilia, we focused our efforts on a painting group of senior citizens, with whom we carried out a series of activities aimed at improving public awareness related to greenery and nature-based solutions, not only of the group’s members, but extending our activities to residents and different age groups during the district festival.
Because of the specific NBS interventions in Katowice (small urban fixtures) the activities of local Place Lab go far beyond their reach. They are the mixture of different type of actions to increase eco-sensitivity of citizens, show social & economic benefits, recognize the local gender issue and the political aspect of NBS. That is why we foreseen: lectures, workshops, meetings, commented walks, site visits, conference, artistic work, festival, exhibition, indoor and outdoor activities for children, joint small NBS intervention, green rehabilitation room actions etc.
NBS implementation
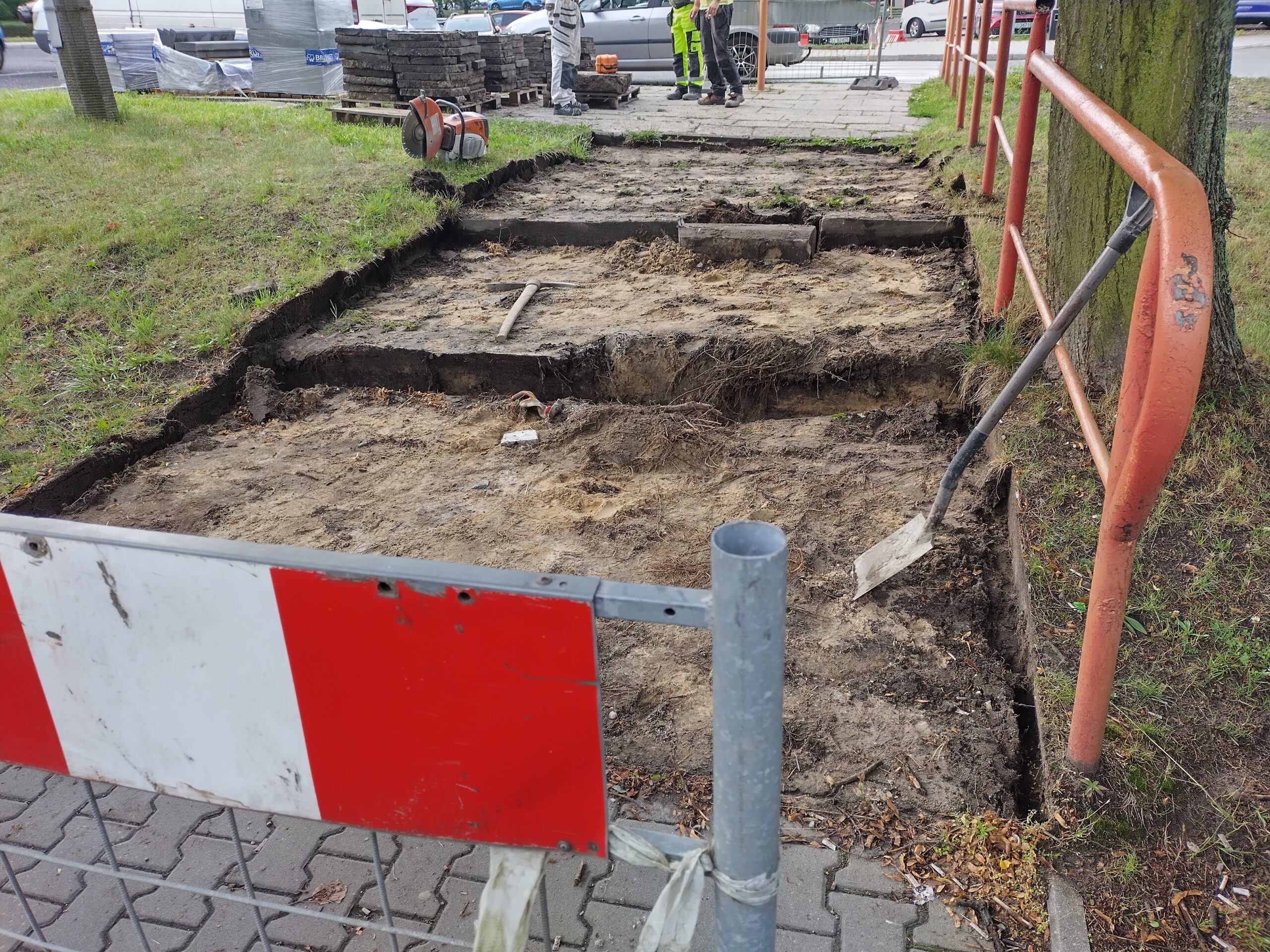
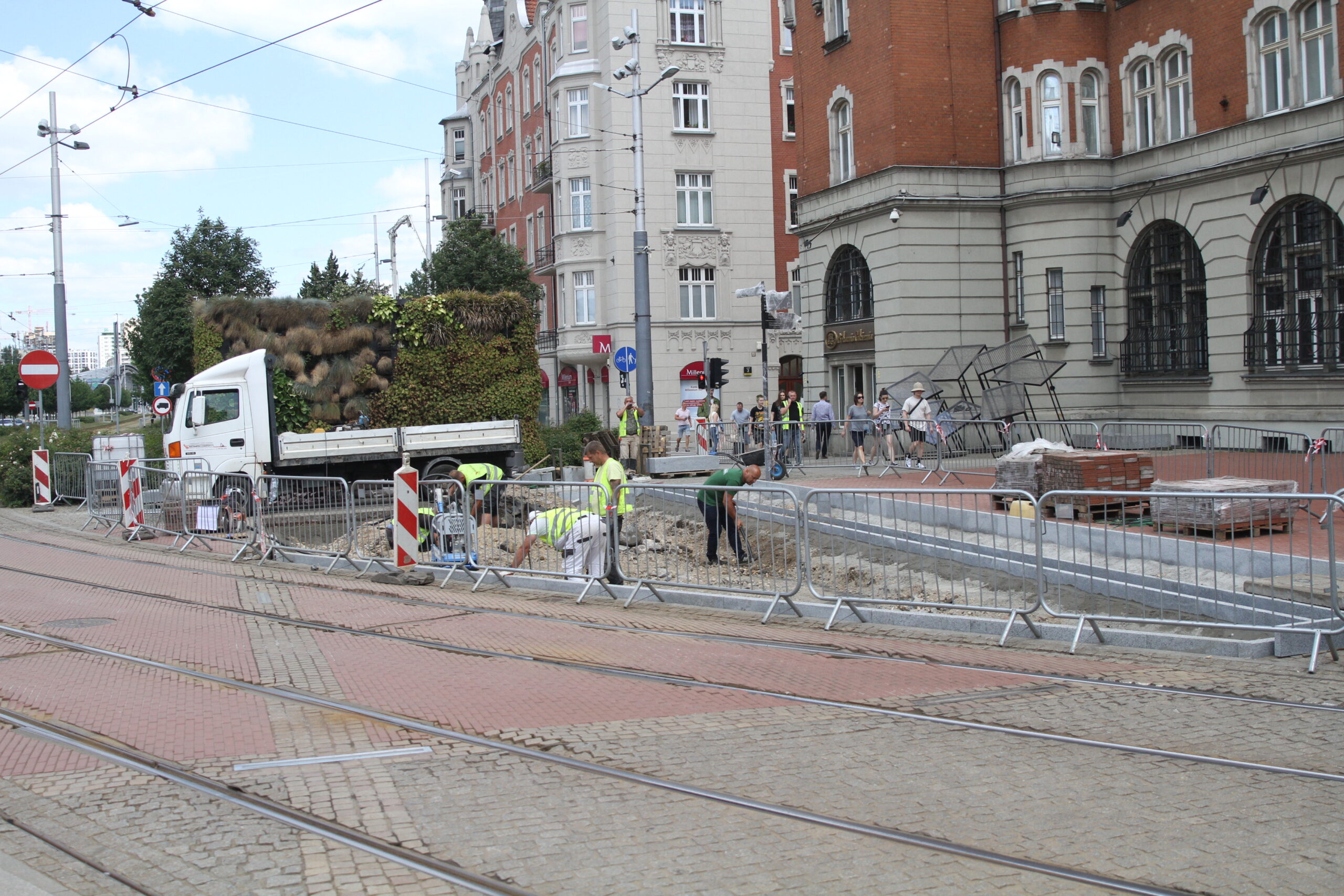
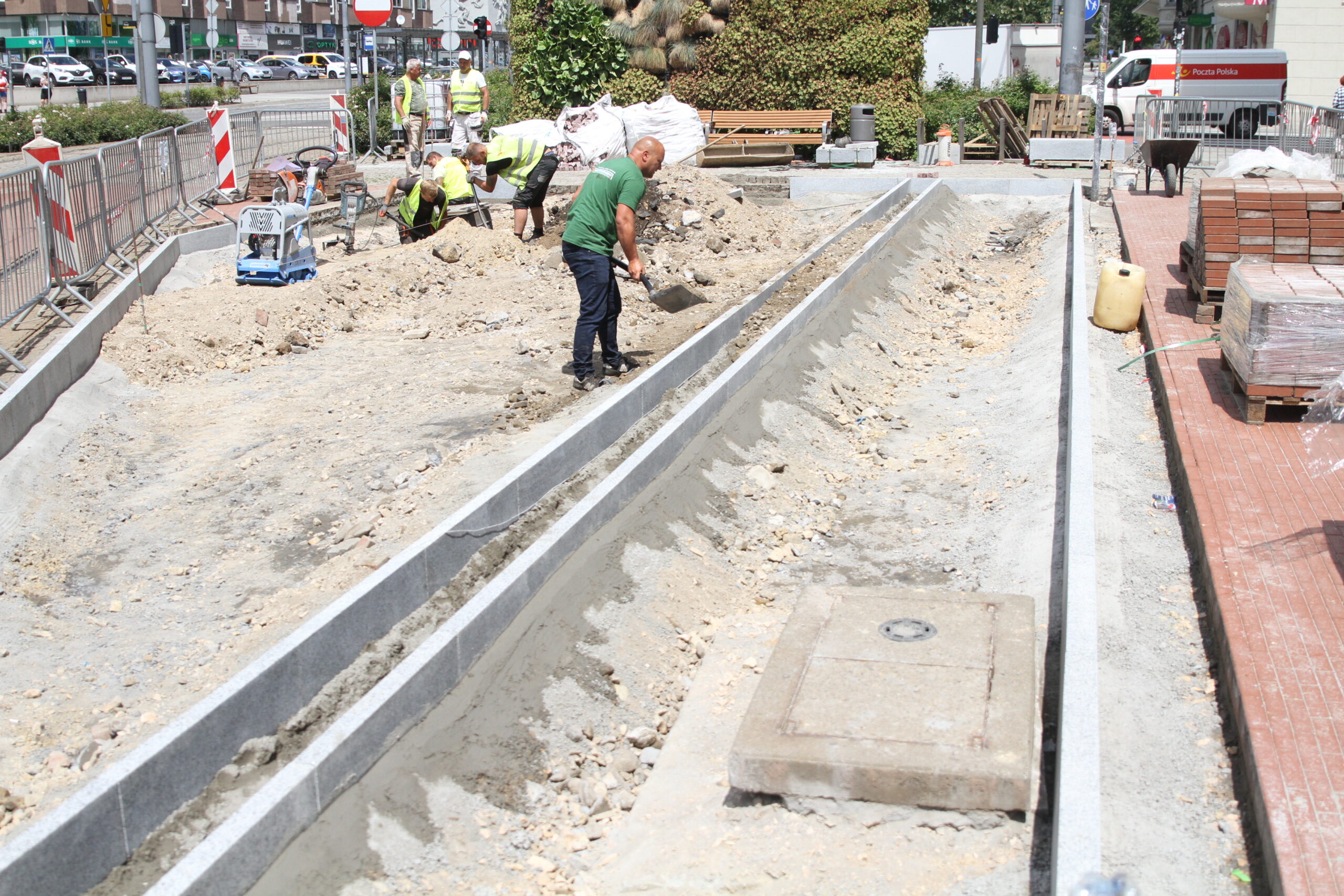
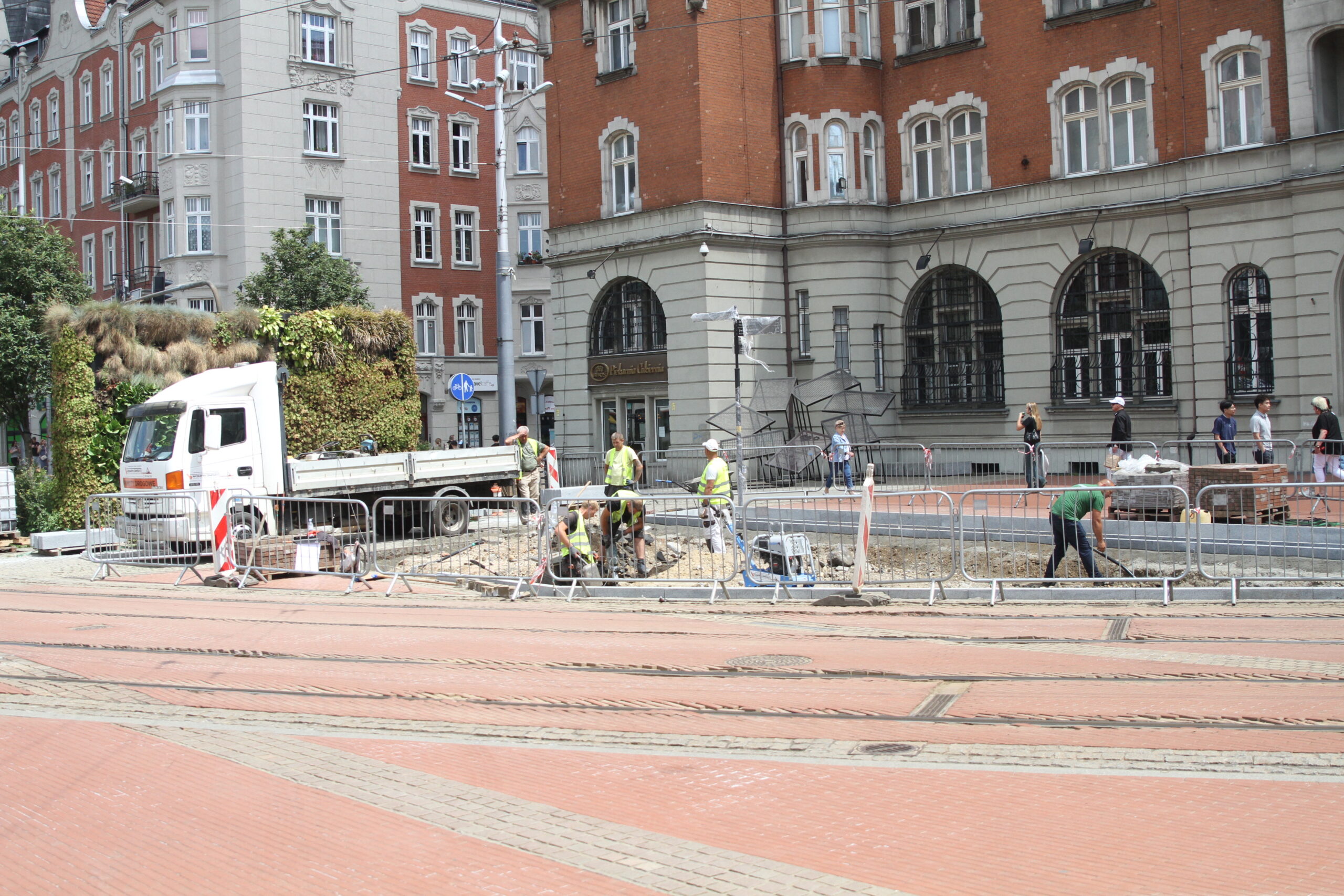
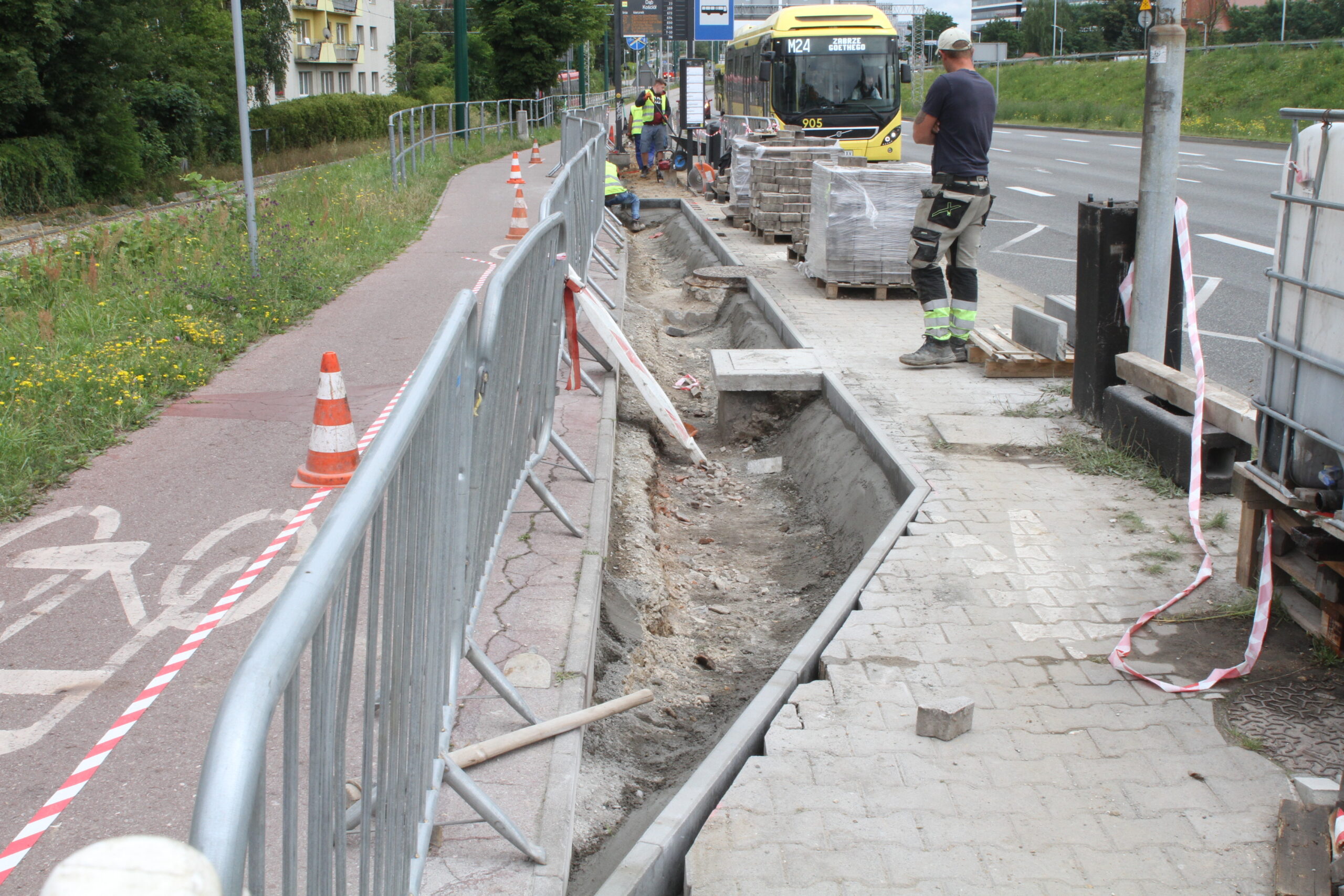
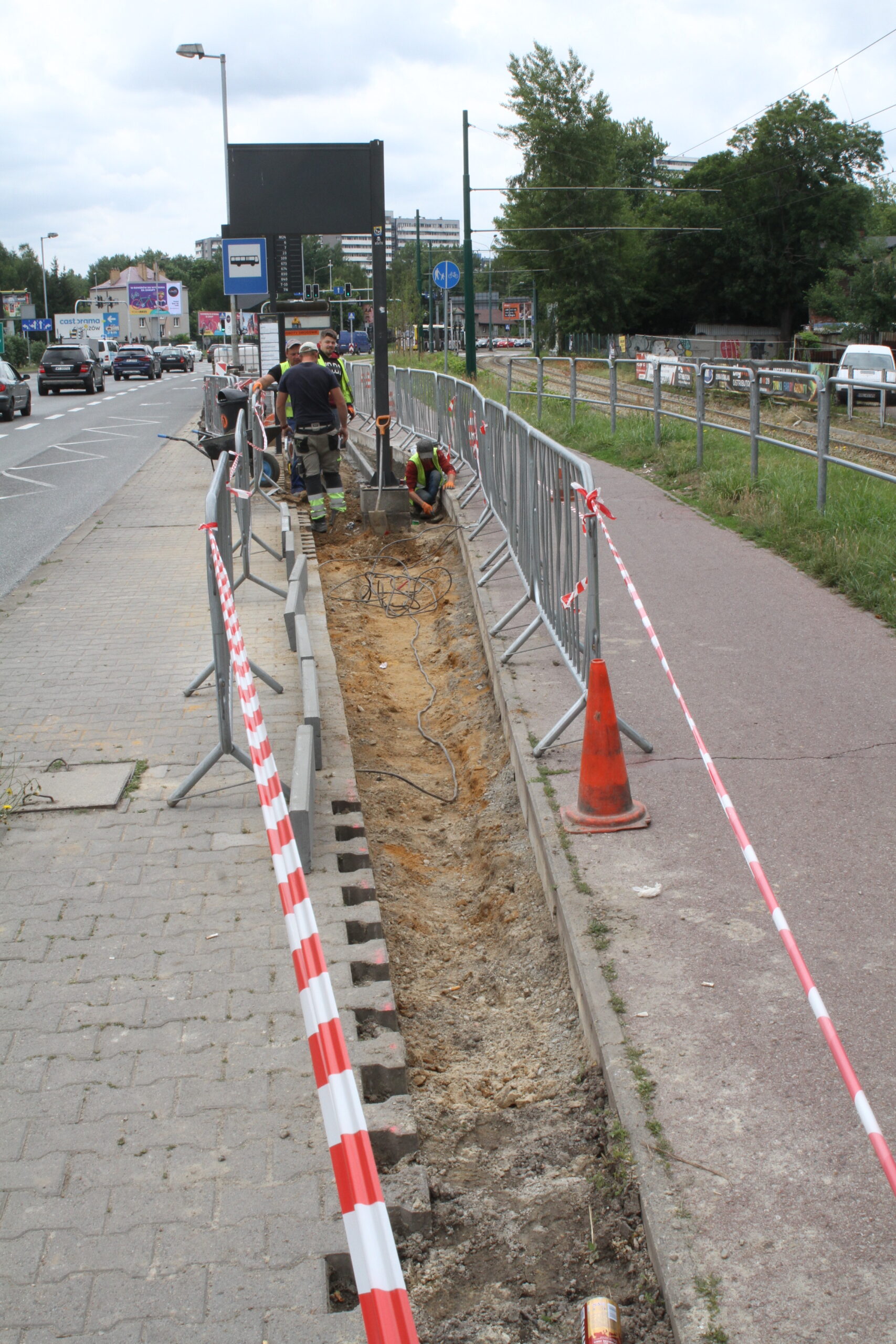
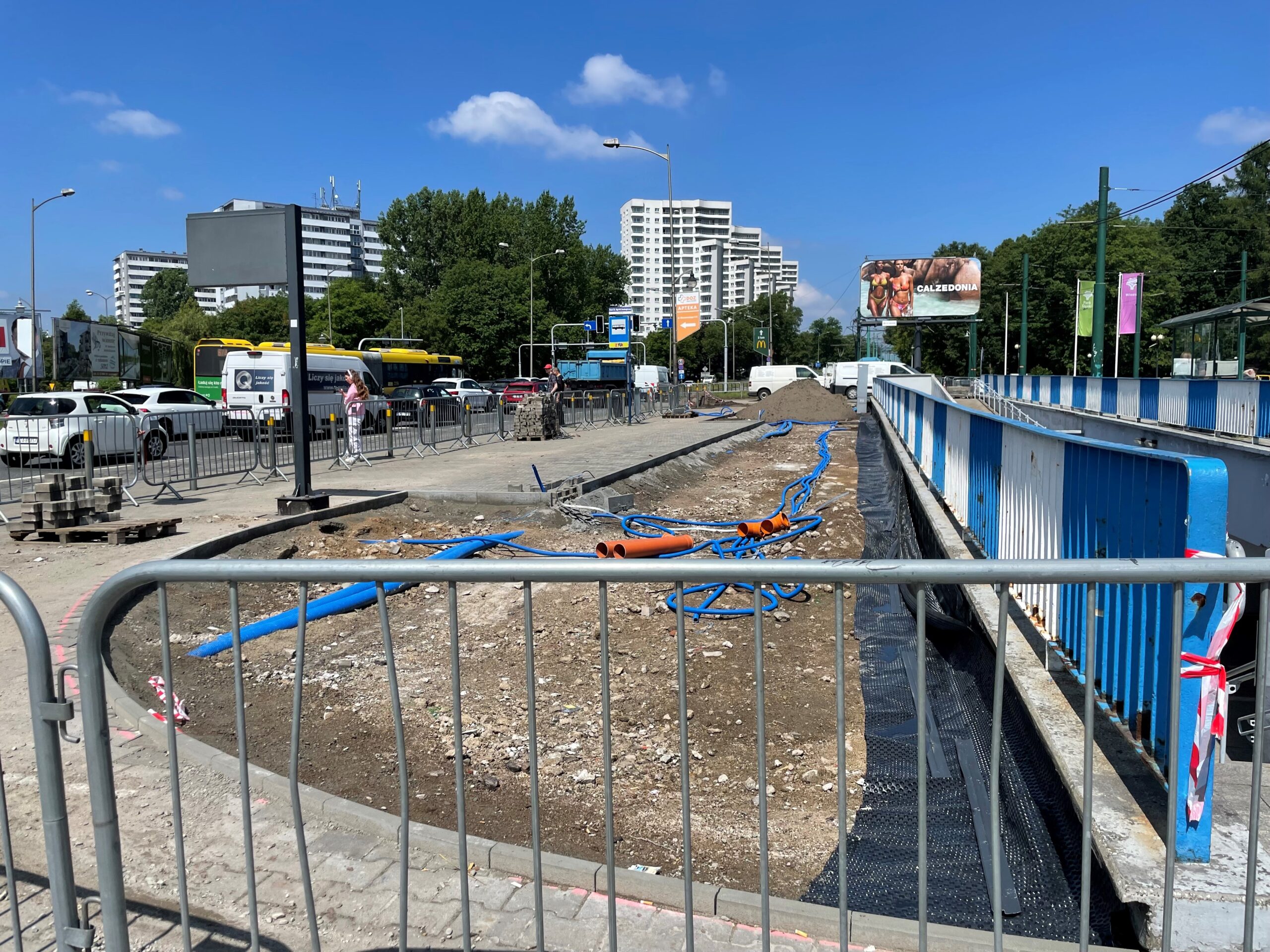
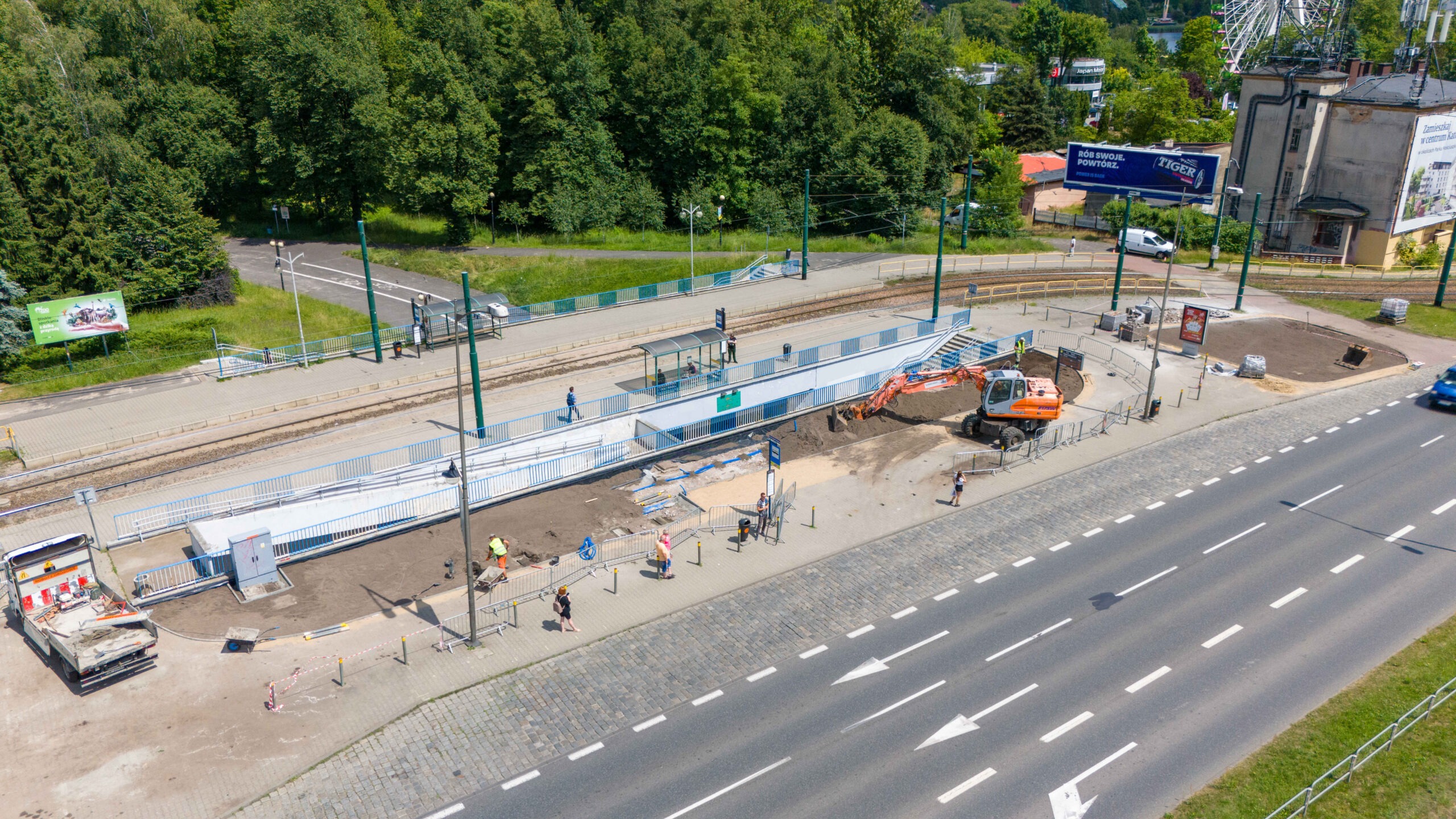
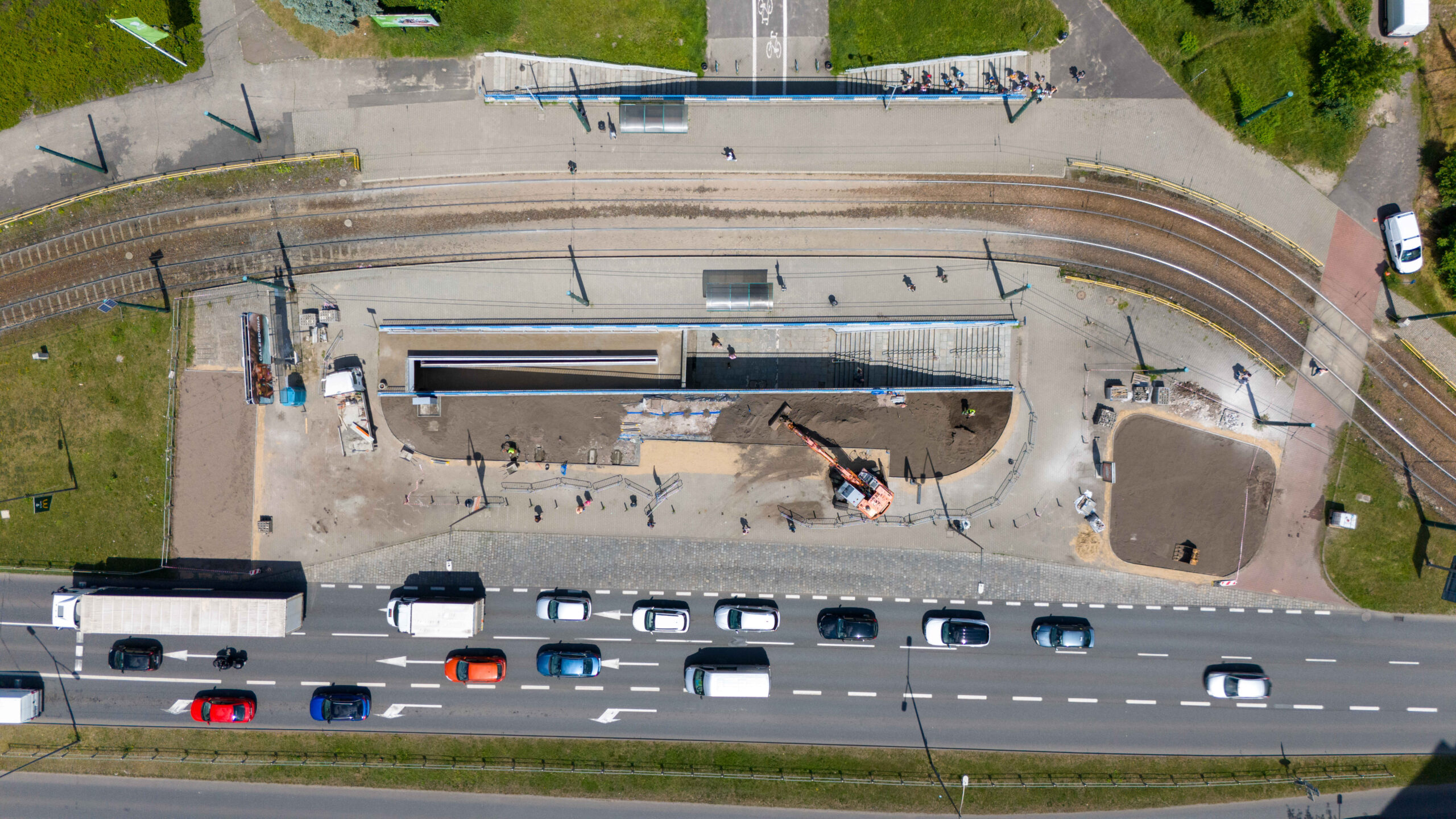
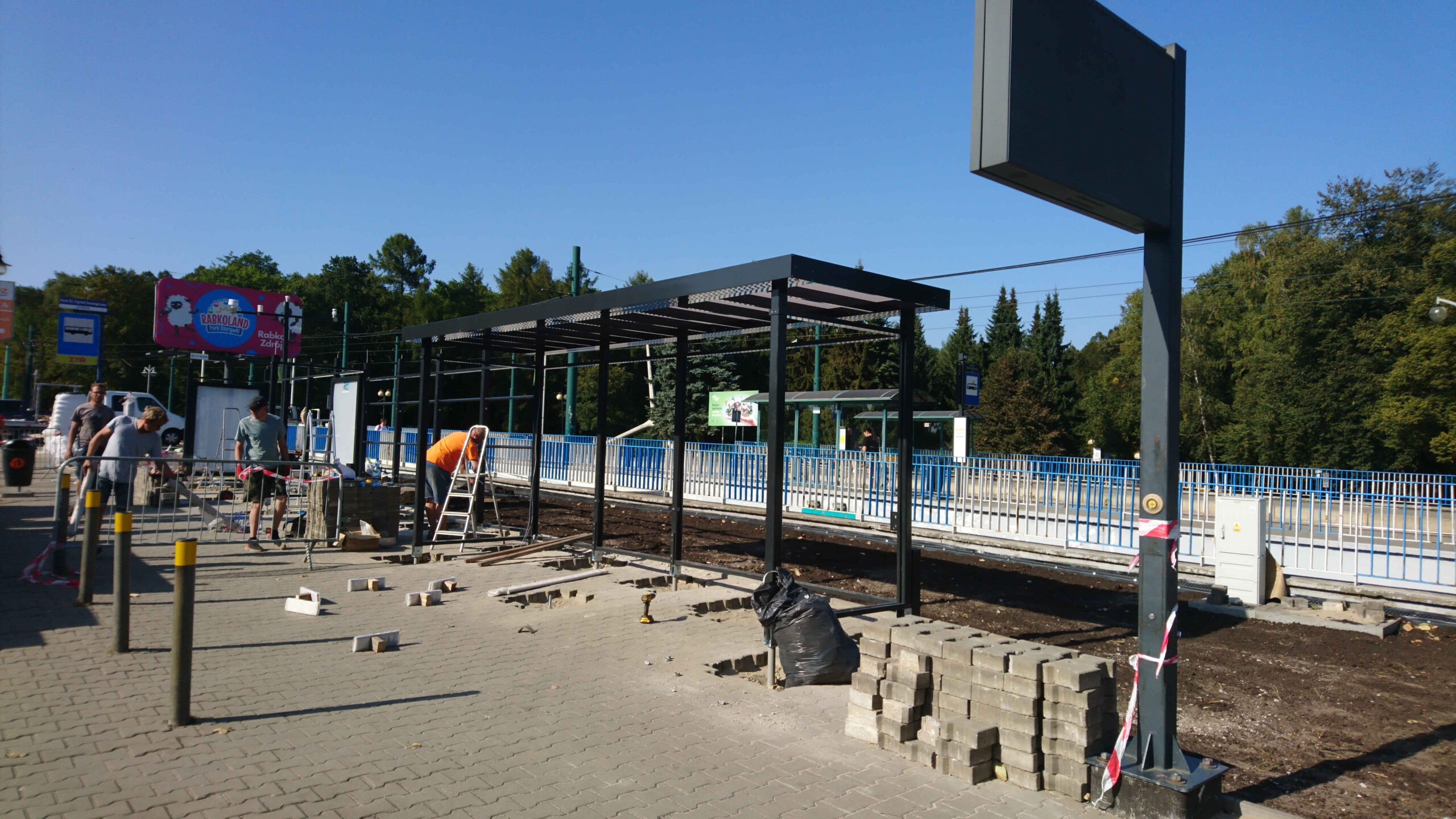
After the completion of the tender procedure and the selection of the contractor in spring 2024 in Katowice, intensive work began on 5 public transport stops, which will be an example of implementation of nature-based solutions as part of the UPSURGE project. First, the old bus stop shelters were dismantled and all the paving work was done, preparing the locations for the designed plantings. The sites will be equipped with specialised sensors, which will be mounted on poles at the stop, as well as digitalisation equipment and passenger information boards. Due to the installation of these facilities, a major challenge was connecting power on time, as well as adapting the electrical connections to the requirements of the installed equipment.
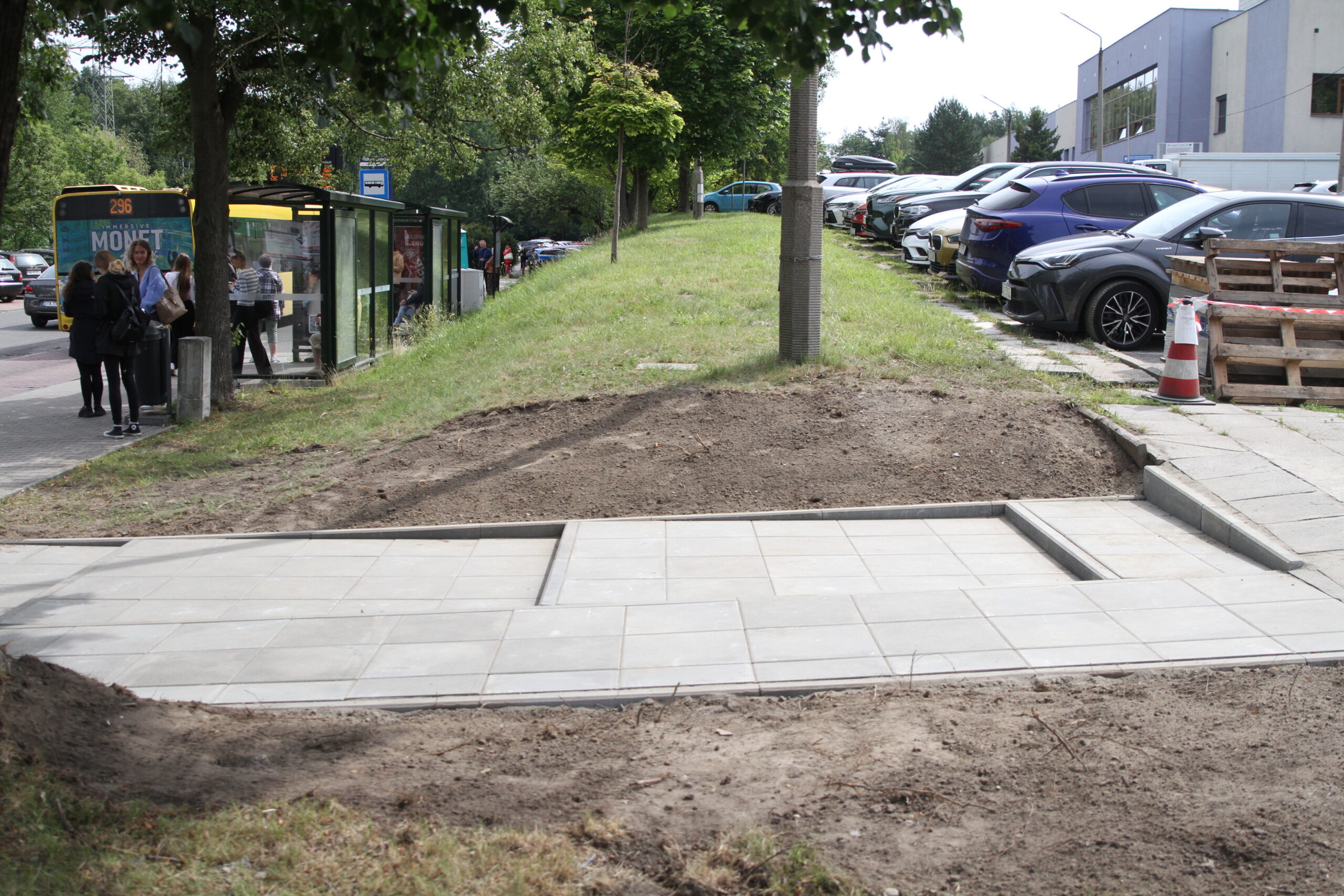
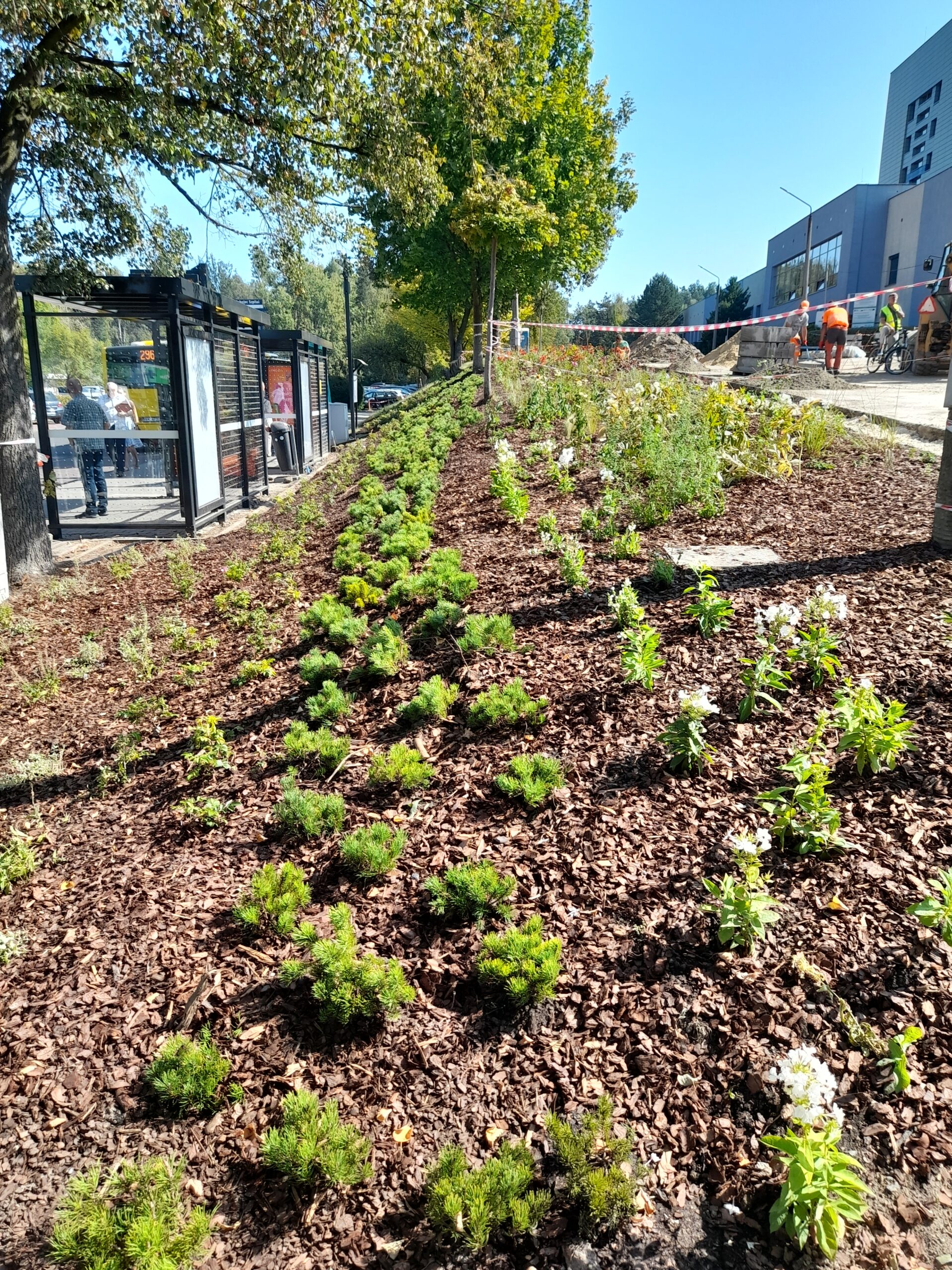
By the end of August 2024, new bus stop shelters with green roofs will be installed in four and street furniture will be installed in five locations in Katowice. In the second half of September, after the hot and dry weather has passed, greenery management and plant care work will be carried out. Ornamental plants, native perennials, low shrubs, grasses, vines, and plants recommended by the UPSURGE project will be planted. By the end of September 2024, the new bus stops will be ready. Thanks to this “unpaving,” the permeable surface area will increase by a total of 570 m². On a city-wide scale, this is not much, but with the high level of surface sealing, every square meter of unpaved area is very significant.
It is worth noting that many suggestions and ideas from local residents were used when designing the bus stops in the UPSURGE project. There were many obstacles and each location had to face different challenges. Three workshops were held for each location, during which the designers presented the prepared concepts and discussed the changes together with the residents. The effects of implementing these activities in Katowice are already visible in the following demo sites.
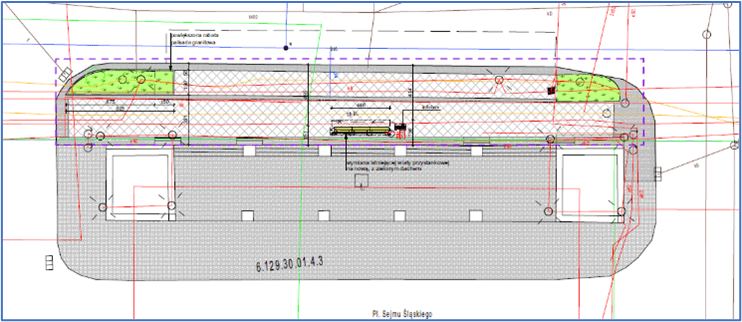
Ochojec Hospital bus stop
This is where the existing bus stop shelters are being replaced with new ones with a green roof. As this is a bus stop used mainly by patients visiting the hospital and nearby health centres, more benches will be installed – some with backrests and armrests, and some in the form of the so-called squats. As part of the investment, a staircase with a handrail has also been upgraded to accommodate people with disabilities (a ramp).
As part of testing of a model solution to reduce the temperature of the urban area, a sensor and an infobox displaying the measurements will be installed at the bus shelter at a height of approximately 3m by the end of August 2024. The biggest challenge at this site was getting the power connections on time.
A unique space full of greenery will be created in the vicinity of the bus stop. Trees providing shade will be planted next to it, as well as shrubs, perennials and ornamental plants resistant to air pollution and periodic droughts.
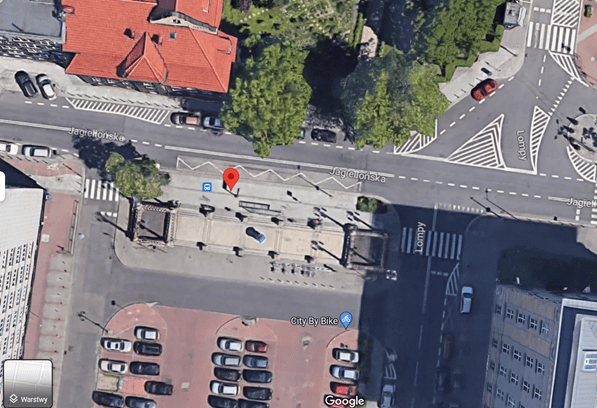
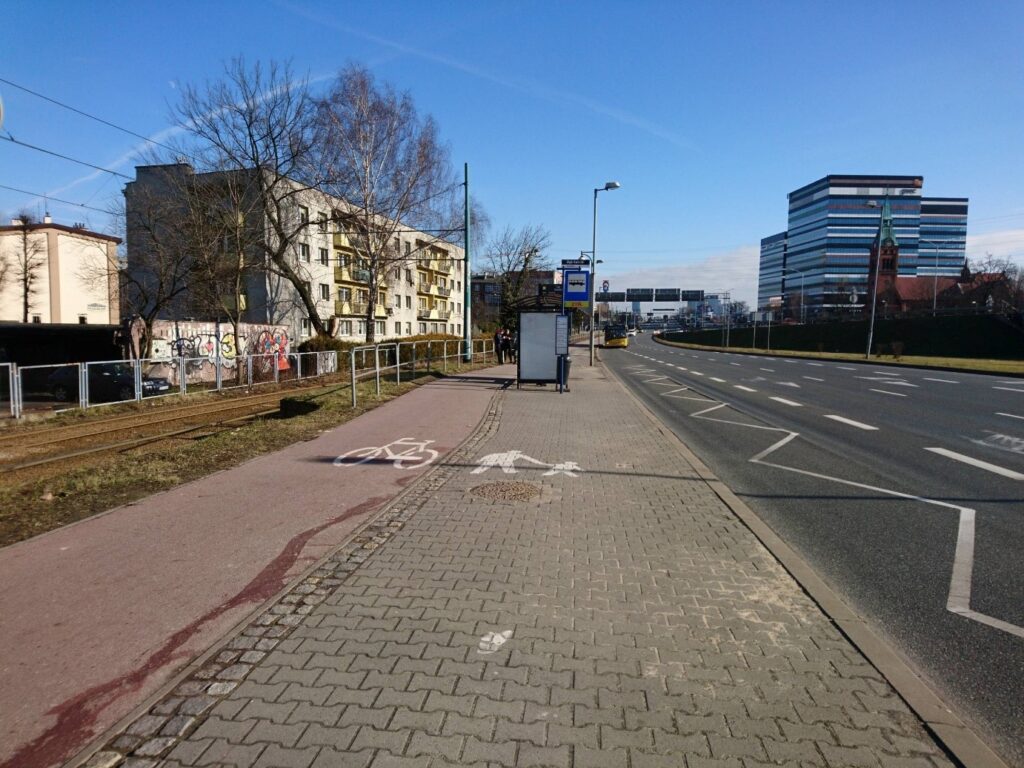
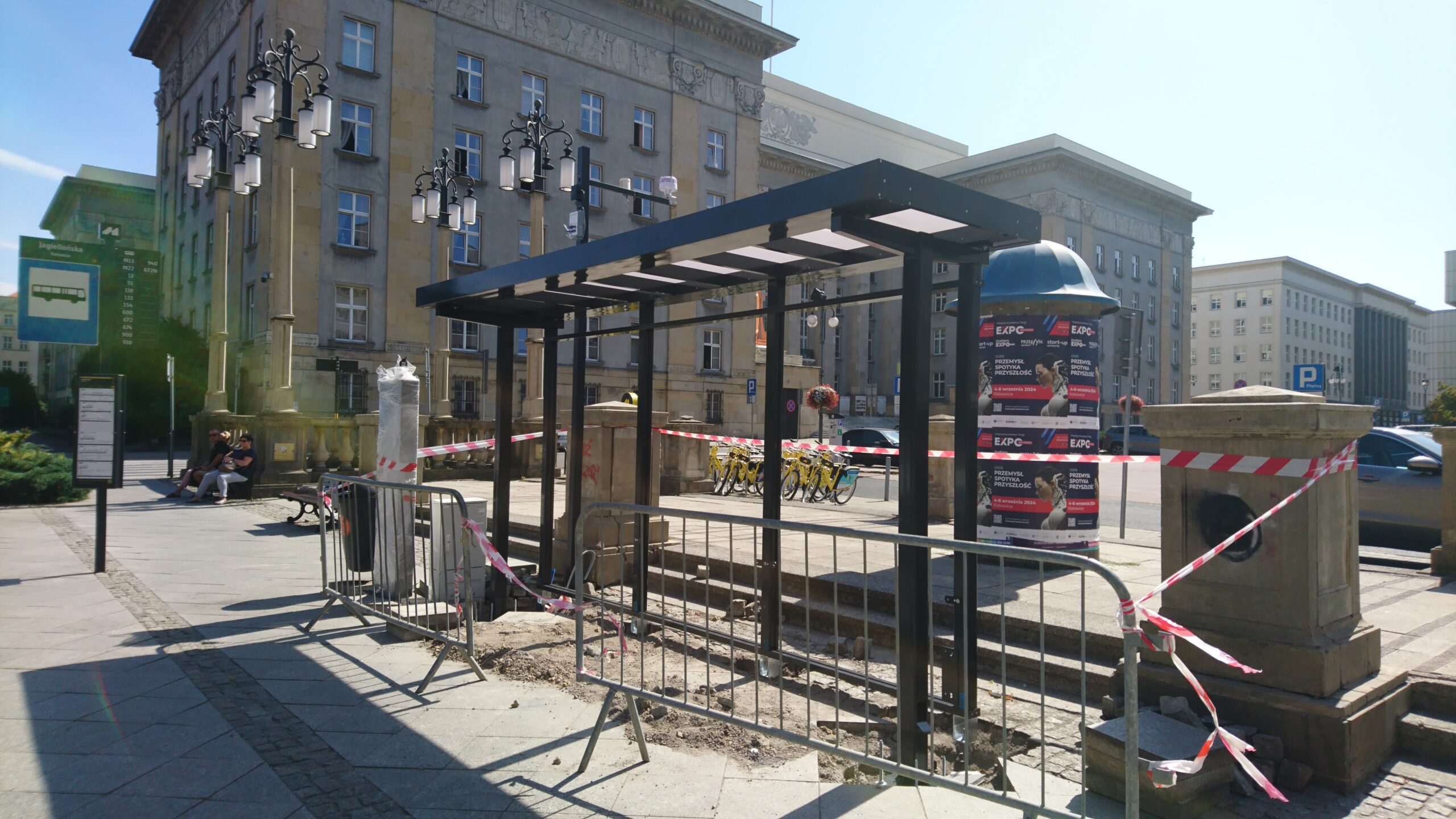
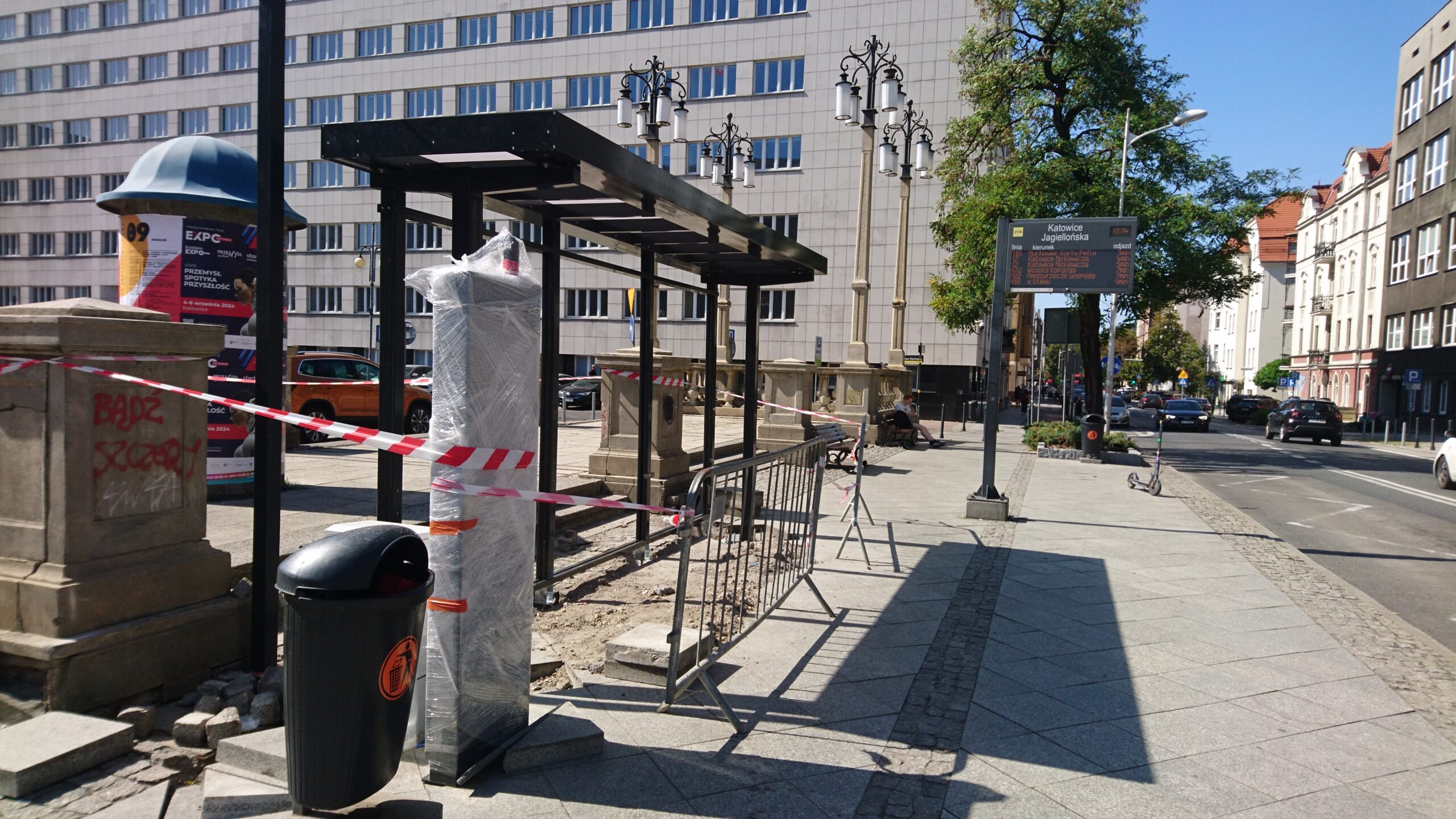
Jagiellońska bus stop
The site is a real challenge, due to its location amidst high density housing, the presence of dense urban infrastructure and the need to adapt to the requirements of the site due to the presence of underground networks, as well as the narrow space – the pavement must remain within the regulatory dimensions. An old bus shelter has been dismantled at the site and will be replaced with a new one with a green roof.
“Unpaving” a section of the surface in the project area is planned, along with the expansion of the western flowerbed and the introduction of new perennial plants, such as Faassen’s catnip, Euphorbia, Basket of Gold, Woodland Sage, Cambridge Geranium, Perennial Cornflower, Sedum and Common Ivy.
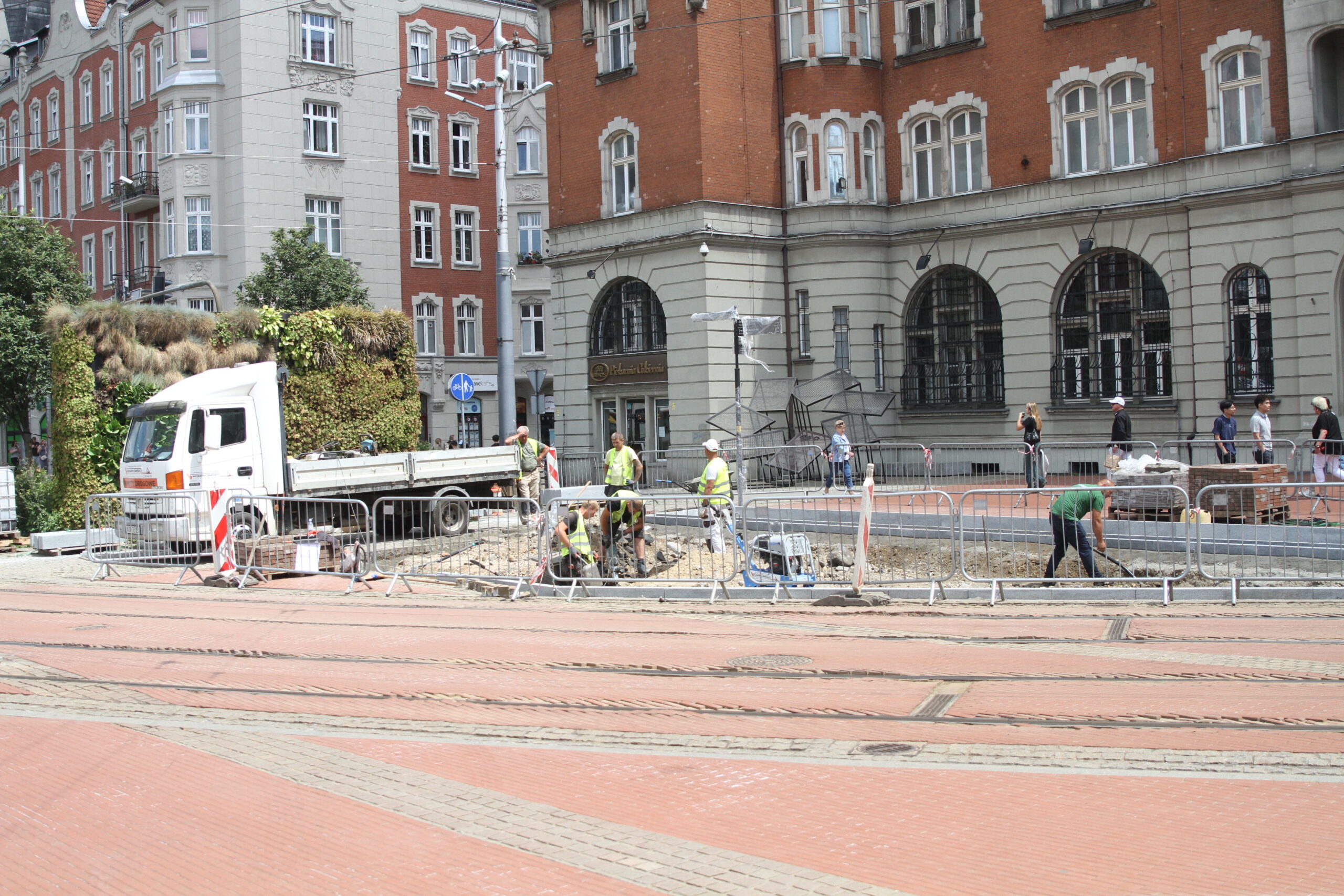
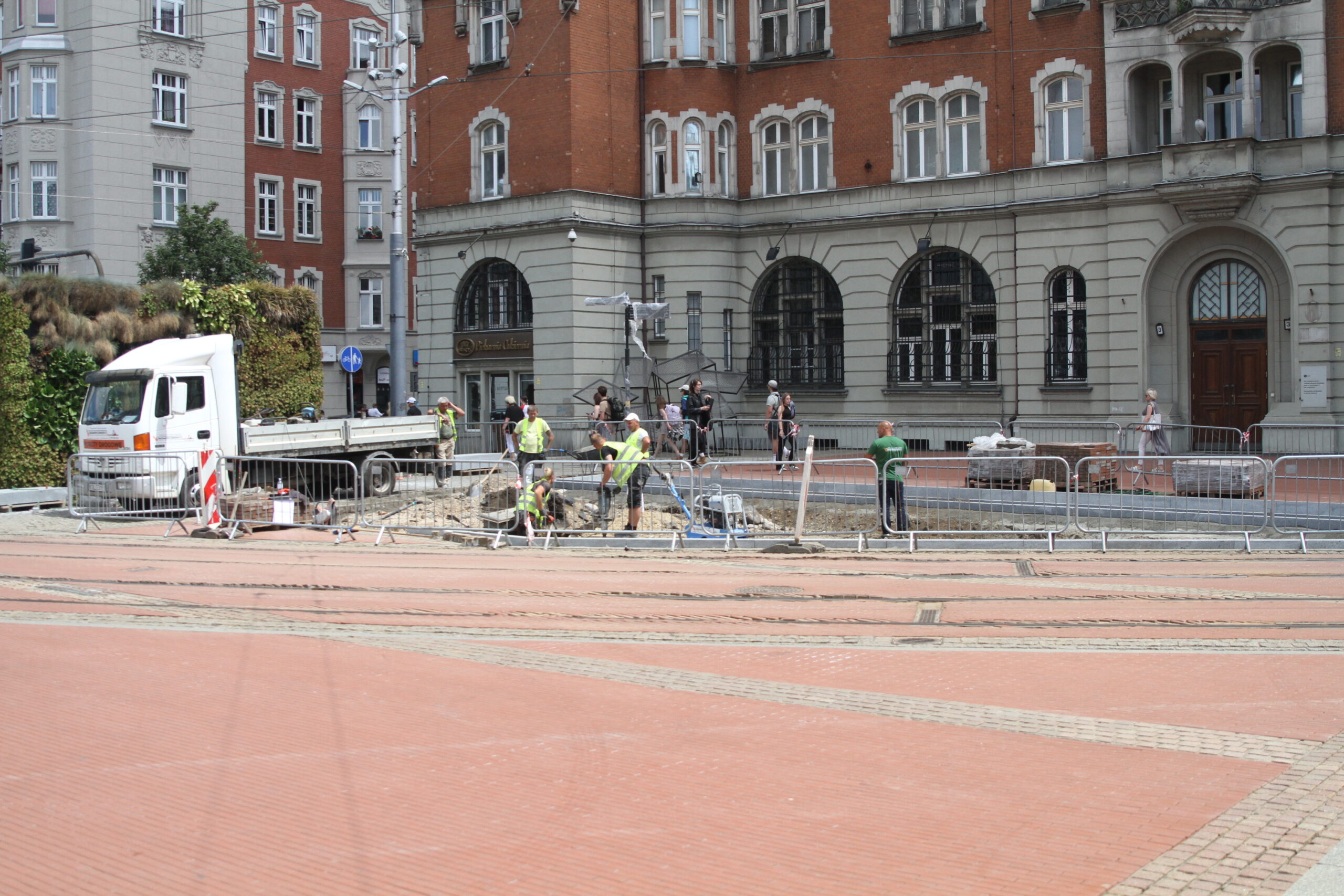
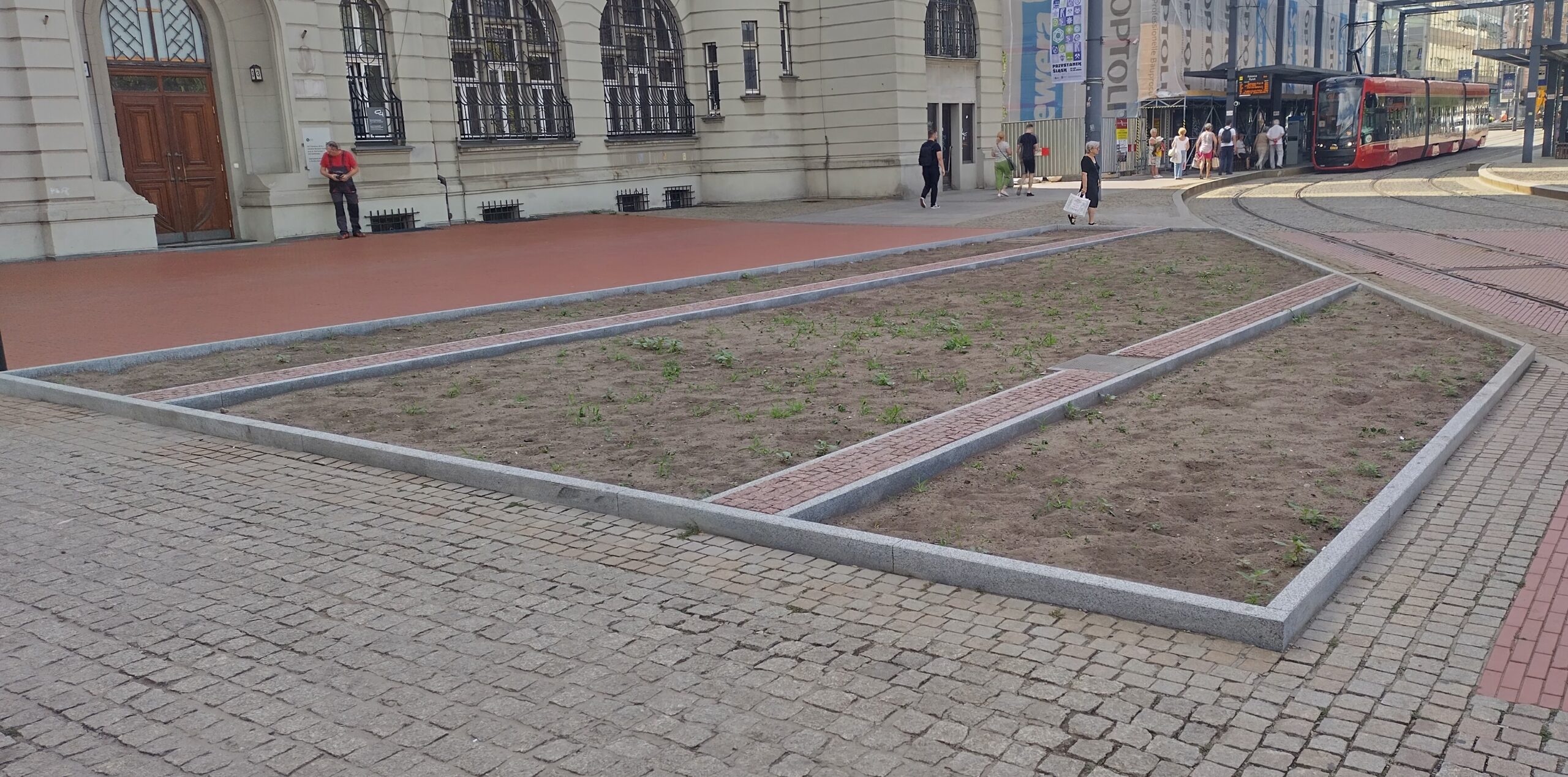
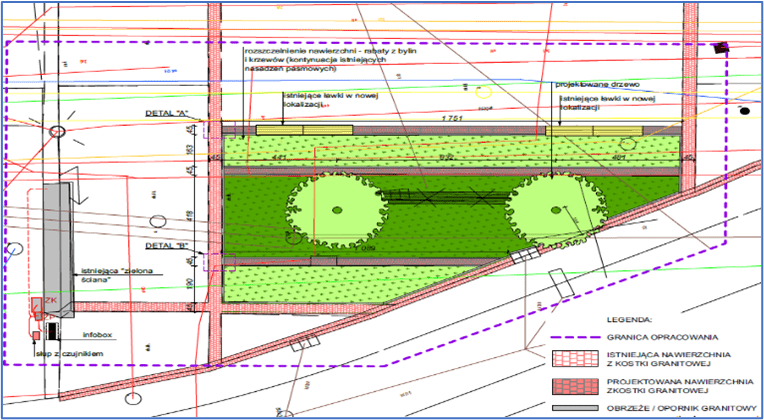
Green market square
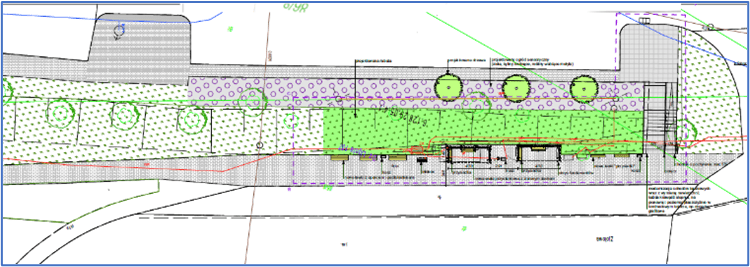
A section of the surface (102 m²) was unpaved to enhance the area with new nature-based solutions (NBS). The paving works were completed in July 2024. Three flowerbeds were created in a strip layout, following the existing arrangement in the western part of the square. The edges of the flowerbeds are bordered with granite blocks, as a continuation of the pattern on the square’s surface Two hornbeams will be planted in one of the flowerbeds in mid-September. In the other flowerbeds, ornamental shrubs such as winged spindle and dwarf mountain pine will be planted, along with perennials such as iris, Cambridge geranium, blazing star, and lady’s mantle, as well as perennial grasses. Benches placed near the flowerbeds will allow residents to relax in the green zone.
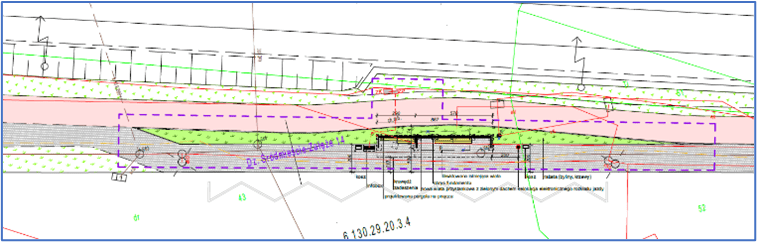
Oak church bus stop
The bus stop is located at a very busy street, in a paved area that hinders rainwater drainage. In accordance with the planned project, the existing bus stop shelter was dismantled and will be replaced in the coming days with a shelter with a green roof. In July 2024, all paving work was completed. A 30 m² section of the surface was unpaved, and a flowerbed was prepared for the planned plant composition. By September, ornamental shrubs, perennials, grasses, and vines will be planted.
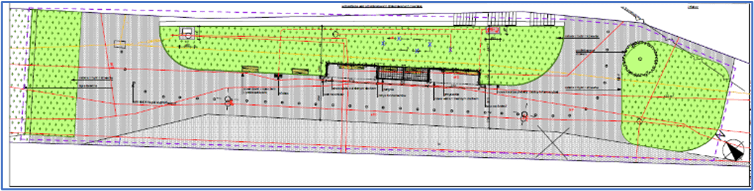
Silesian Park Zoological Garden bus stop
The NBS implemented at the Silesian Park Zoological Garden bus stop at Chorzowska Street covers the largest area of unpaved surface, at a total of 418 m2. The proposed solutions are a real challenge for the existing problems. This is a place used by many passengers visiting the Silesian Park where, despite its proximity to green areas, it is very hot and lacks shelter.
The old bus stop shelter has been dismantled and will be replaced by a new one with a green sedum roof by the end of July 2024. The bus stop shelter will be integrated with a pergola shade on which vines will grow. Plants will be planted around the shelter to create a landscaped green zone with an ecological and aesthetic function.
In the first phase, paving works were also carried out to prepare the space for a new flowerbed of approximately 215 m2. Space was also prepared for additional flowerbeds extending the lawn on both sides of the bus stop – approximately 75 m2 and 115 m2 respectively. The edges of the flowerbeds will be bordered with concrete lawn edging. The flowerbeds will be planted with shrubs such as rose, winged spindle, and black elder, perennials such as feather reed grass, woodland sage, sedum, and Faassen’s catnip, as well as bulbous plants such as daffodil and garlic. The greenery in this area will positively impact the microclimate of the site and improve its environmental parameters, while at the same time increasing biodiversity.
As at all sites, a sensor and a free-standing infobox displaying the measurements will be installed in August 2024.